ADHD in Adults: Symptoms and Strategies
Introduction:
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is often associated with childhood, but it can persist into adulthood, impacting various aspects of life. Adults with ADHD may face challenges with attention, focus, organization, and impulse control. While the symptoms might manifest differently in adults than in children, they can still significantly impact daily living, work, relationships, and overall well-being. Recognizing the signs and understanding effective strategies is crucial for adults with ADHD to manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives.
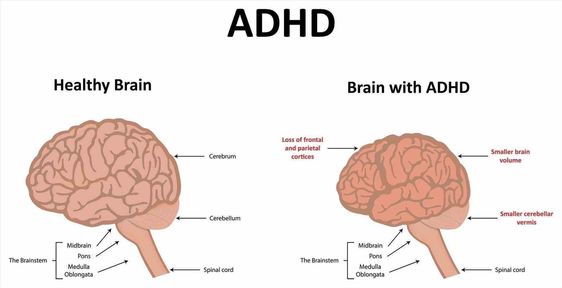
This article delves into the common symptoms of ADHD in adults and explores practical strategies to navigate the challenges it presents. From understanding the different types of ADHD to implementing organizational techniques and seeking professional support, this comprehensive guide aims to empower adults with ADHD to thrive in their personal and professional lives.
Recognizing ADHD in Adulthood
ADHD symptoms in adults can be subtle and easily mistaken for other conditions like anxiety or mood disorders. Some common indicators include:
- Difficulty focusing and sustaining attention: This might manifest as trouble concentrating during meetings, struggling to follow instructions, or frequently getting sidetracked.
- Disorganization and poor time management: Adults with ADHD may find it challenging to prioritize tasks, meet deadlines, or keep track of appointments.
- Impulsivity: This can range from interrupting conversations to making rash decisions without considering the consequences.
- Restlessness and fidgeting: Adults may feel a constant need to move or feel internally restless.
Strategies for Managing ADHD
Living with ADHD can be challenging, but several strategies can help manage symptoms and improve daily life:
- Seek professional diagnosis and treatment: A mental health professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate interventions, such as therapy or medication.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT can help individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and develop coping mechanisms for managing impulsivity and improving focus.
- Organizational tools and techniques: Utilizing calendars, planners, and reminder apps can improve time management and organization.
- Lifestyle modifications: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep can positively impact ADHD symptoms.
- Support groups and communities: Connecting with others who understand the challenges of ADHD can provide valuable support and shared experiences.

.jpg)