Introduction
Robotic surgery, a cutting-edge surgical approach, has revolutionized the medical field, offering a minimally invasive alternative to traditional open surgeries. This innovative technology allows surgeons to perform complex procedures with enhanced precision, dexterity, and control, resulting in numerous benefits for patients.
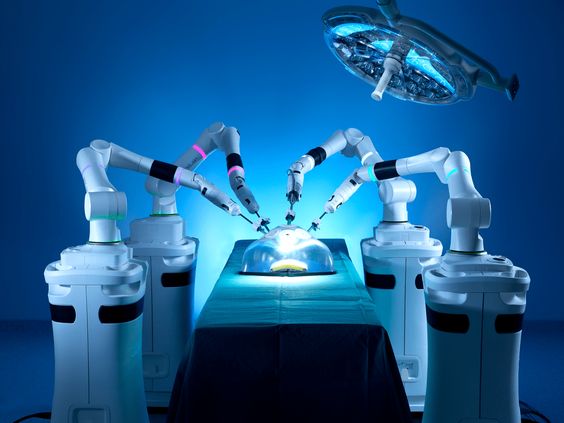
Robotic surgical systems typically consist of a surgeon’s console, a patient-side cart with multiple robotic arms, and a high-definition 3D vision system. The surgeon sits at the console, remotely controlling the robotic arms, which hold surgical instruments and a camera, while viewing a magnified, three-dimensional image of the surgical field.
Advancements in Robotic Surgery
Over the years, robotic surgery has witnessed remarkable advancements, further enhancing its capabilities and expanding its applications.
Enhanced Precision and Dexterity
One of the most significant advancements is the development of robotic arms with seven degrees of freedom, mimicking the natural movements of the human wrist and surpassing the limitations of traditional laparoscopic instruments. This enhanced dexterity allows surgeons to navigate intricate anatomical structures with greater ease and perform complex maneuvers with utmost accuracy.
Improved Visualization and Imaging
Advancements in imaging technology have also played a crucial role in the evolution of robotic surgery. High-definition 3D cameras provide surgeons with an immersive and magnified view of the surgical field, enabling them to visualize delicate tissues and structures with exceptional clarity. Real-time image guidance systems further enhance surgical precision by overlaying pre-operative images onto the live surgical view, aiding in tumor localization and critical structure avoidance.
Expanding Applications
Robotic surgery has rapidly gained acceptance across various surgical specialties, including urology, gynecology, cardiac surgery, and general surgery. Its applications continue to expand as technology advances, with procedures such as prostatectomies, hysterectomies, heart valve repairs, and hernia repairs becoming increasingly common.

.jpg)