Introduction
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition that causes pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and arm. It occurs when the median nerve, which runs from your forearm into your hand, becomes compressed at the wrist.
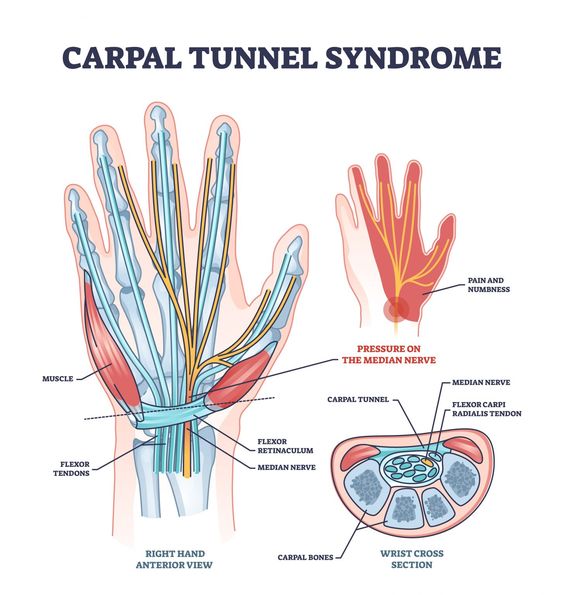
The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway surrounded by bones and ligaments on the palm side of your hand. When the median nerve is compressed, it can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
- Numbness or tingling in the thumb and index, middle, and part of the ring fingers
- Pain in the hand and wrist, which may travel up the arm
- Weakness in the hand, making it difficult to grip objects
- A feeling of swelling in the fingers
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
The symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome often start gradually and may be worse at night. You may notice that your symptoms are worse after you’ve been using your hands a lot, such as when driving, typing, or holding a phone.
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Anything that reduces the amount of space in the carpal tunnel can cause carpal tunnel syndrome. Some common causes include:
- Repetitive hand movements. People who perform repetitive hand movements, such as typing, assembly line work, or playing certain musical instruments, are at increased risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Pregnancy. Fluid retention during pregnancy can compress the median nerve.
- Obesity. Being overweight or obese increases your risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Medical conditions. Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and thyroid disease, can also contribute to carpal tunnel syndrome.
Treatment for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
The goal of treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome is to relieve pressure on the median nerve. Treatment options include:
- Wrist splints. Wearing a wrist splint at night can help prevent you from bending your wrist, which can compress the median nerve.
- Medications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help reduce pain and swelling. In some cases, your doctor may inject corticosteroids into the carpal tunnel to reduce inflammation.
- Therapy. Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles in your hand and wrist and improve your range of motion.
- Surgery. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the median nerve.
If you have symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome, see your doctor to get a diagnosis and discuss treatment options. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent permanent nerve damage.

.jpg)