Contact Dermatitis: Symptoms, Causes, Types & Treatments
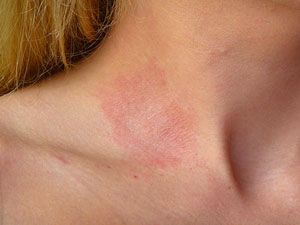
Contact dermatitis is a common skin condition characterized by inflammation of the skin due to exposure to certain irritants or allergens. It can cause discomfort, itching, and redness. Let’s explore the symptoms, causes, types, and available treatments for contact dermatitis.
Introduction
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin comes into direct contact with substances that trigger an immune response. These substances can be irritants (such as chemicals, soaps, or detergents) or allergens (such as plants, metals, or fragrances). The condition can affect anyone, but some individuals are more prone to it due to genetic factors or repeated exposure.
Symptoms
The symptoms of contact dermatitis may vary depending on the type and severity of the reaction. Common symptoms include:
- Redness and Rash: Affected areas of the skin become red, swollen, and itchy.
- Blisters: In severe cases, fluid-filled blisters may develop.
- Dry, Cracked Skin: Prolonged exposure to irritants can lead to dryness and cracking.
- Burning or Stinging Sensation: The affected skin may feel uncomfortable or painful.
Causes
- Irritant Contact Dermatitis:
- Caused by direct exposure to irritants like detergents, solvents, or acids.
- Common in occupations involving frequent handwashing or chemical handling.
- Allergic Contact Dermatitis:
- Triggered by allergens such as poison ivy, nickel, or fragrances.
- Develops after repeated exposure, leading to sensitization.
Types
- Acute Contact Dermatitis:
- Occurs shortly after exposure to an irritant or allergen.
- Symptoms appear within hours to a few days.
- Chronic Contact Dermatitis:
- Develops over time due to repeated exposure.
- Symptoms persist for weeks or months.
Treatments
- Avoidance:
- Identify and avoid the triggering substances.
- Use protective measures (gloves, barrier creams) when handling irritants.
- Topical Treatments:
- Apply corticosteroid creams to reduce inflammation.
- Use emollients to soothe dry skin.
- Oral Medications:
- Antihistamines for itching.
- Steroids (systemic) for severe cases.
- Wet Dressings:
- Soak affected areas in cool water and apply wet dressings to relieve symptoms.
Remember to consult a dermatologist for personalized advice and treatment options. Contact dermatitis can significantly impact your quality of life, but with proper management, you can find relief and prevent future flare-ups.

.jpg)