Introduction
Gangrene is a serious condition that occurs when blood flow to a certain area of the body is interrupted, leading to tissue death. It is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment to prevent potentially life-threatening complications.
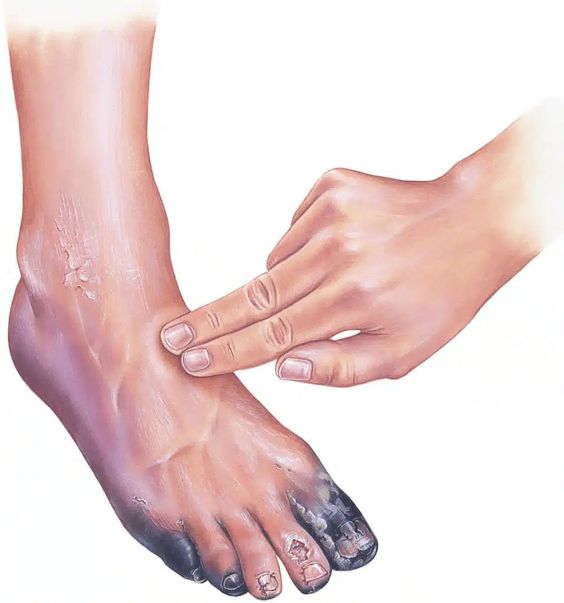
Gangrene can affect various body parts, including the toes, fingers, limbs, and internal organs. The affected area often appears discolored, ranging from pale to blue, purple, or black. Other symptoms include numbness, pain, swelling, and a foul odor emanating from the affected area.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the definition, symptoms, treatment, and causes of gangrene, equipping you with the knowledge to recognize this condition and seek prompt medical attention.
What is Gangrene?
Gangrene is a serious medical condition characterized by the death of body tissue due to a lack of blood supply. The affected tissue gradually deteriorates and can lead to amputation if left untreated.
Symptoms of Gangrene
The symptoms of gangrene vary depending on the location and severity of the condition. Common signs include:
- Discoloration of the skin: The affected area may turn pale, blue, purple, or black.
- Numbness and tingling: Loss of sensation in the affected area is a common symptom.
- Intense pain: Some individuals experience severe pain, while others may experience little to no pain.
- Swelling: The affected area may become swollen and tender.
- Foul odor: A distinctive, unpleasant odor may emanate from the affected area.
- Drainage: Pus-filled blisters or sores may develop and drain fluid.
Treatment for Gangrene
Prompt treatment is essential to prevent the spread of gangrene and save the affected tissue. Treatment options typically include:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the dead tissue, also known as debridement, is often necessary. In severe cases, amputation may be required.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are used to treat underlying infections that may be contributing to gangrene.
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: This therapy involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber, which helps increase oxygen delivery to the affected tissues.
- Vascular surgery: If gangrene is caused by poor blood flow, vascular surgery may be necessary to improve circulation.
Causes of Gangrene
Gangrene can develop due to various factors that restrict blood flow to body tissues. Common causes include:
- Infection: Bacterial infections can damage blood vessels and disrupt blood flow.
- Injury: Severe injuries, such as burns, frostbite, and crush injuries, can damage tissues and lead to gangrene.
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD): PAD narrows the arteries in the limbs, reducing blood flow to the extremities.
- Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes are more susceptible to gangrene due to poor circulation and nerve damage.
- Blood clots: Blood clots can block blood vessels, leading to gangrene.
Conclusion
Gangrene is a serious medical condition that demands immediate medical attention. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the causes of gangrene are crucial for early detection and treatment. If you suspect you or someone you know may have gangrene, seek medical attention immediately.

.jpg)