Introduction
Pericarditis is an inflammation of the pericardium, the sac-like membrane that surrounds the heart. It can cause chest pain, shortness of breath and other symptoms. Pericarditis is usually caused by a viral infection, but it can also be caused by other factors such as bacterial infections, heart surgery, and certain medications. In most cases, pericarditis is mild and resolves on its own. However, some cases may be more severe and require treatment.
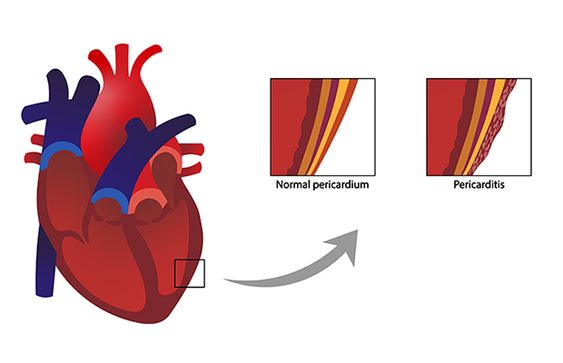
Pericarditis is diagnosed based on symptoms, physical examination, and medical history. Tests such as electrocardiogram (ECG), chest X-ray, and echocardiogram may be used to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment for pericarditis depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition.
Causes of Pericarditis
The most common cause of pericarditis is a viral infection. Other causes include:
- Bacterial infections
- Heart surgery
- Heart attack
- Kidney failure
- Autoimmune disorders
- Certain medications
- Radiation therapy
- Injury to the chest
Symptoms of Pericarditis
The most common symptom of pericarditis is sharp, stabbing chest pain that may worsen with breathing or lying down. Other symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath
- Fever
- Cough
- Fatigue
- Swelling in the legs or abdomen
Treatment for Pericarditis
Treatment for pericarditis depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. In many cases, over-the-counter pain relievers and rest are enough to relieve symptoms. More severe cases may require hospitalization and treatment with medications such as:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Colchicine
- Corticosteroids
If the pericarditis is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics will be prescribed. In some cases, a procedure called pericardiocentesis may be necessary to drain fluid from the pericardium.

.jpg)