Introduction:
Psoriasis is a chronic, autoimmune skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by the rapid buildup of skin cells, leading to thick, scaly patches that can be itchy, painful, and even debilitating in severe cases. While there is no cure for psoriasis, various treatment options are available to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
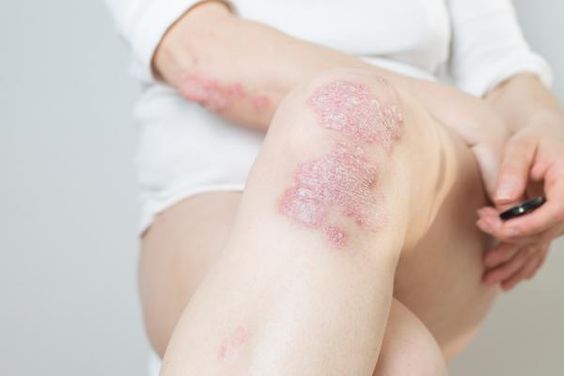
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of psoriasis, exploring its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Whether you are newly diagnosed or seeking a deeper understanding of this complex condition, this article provides valuable insights to help you navigate your psoriasis journey.
Understanding Psoriasis: Causes and Triggers
Psoriasis occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, causing them to multiply rapidly. This accelerated growth cycle leads to the formation of raised, red patches covered with silvery scales. While the exact cause of psoriasis remains unclear, researchers believe that a combination of genetic and environmental factors plays a significant role.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Psoriasis
Psoriasis can manifest differently in each individual, and symptoms can range from mild to severe. Common signs of psoriasis include:
- Red, raised patches of skin: These patches, known as plaques, are typically covered in silvery scales and are most commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and torso.
- Itching and burning: Psoriasis plaques can be intensely itchy and may burn or sting.
- Dry, cracked skin: The affected areas may become dry and cracked, sometimes bleeding.
- Nail changes: Psoriasis can also affect the nails, causing pitting, discoloration, and thickening.
Exploring Treatment Options for Psoriasis
While there is no one-size-fits-all cure for psoriasis, a variety of treatment options can effectively manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment plans are often tailored to the individual, considering the severity of their condition, medical history, and lifestyle factors. Common treatment modalities include:
- Topical treatments: Creams, ointments, and shampoos containing corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, or coal tar can help slow down skin cell growth and reduce inflammation.
- Light therapy: Exposing the skin to controlled amounts of ultraviolet (UV) light can help slow down skin cell growth.
- Systemic medications: For moderate to severe cases, oral or injectable medications may be prescribed to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation.
- Biologics: This newer class of drugs targets specific parts of the immune system involved in psoriasis development.
Living with psoriasis can be challenging, but with proper management and a proactive approach to treatment, individuals with psoriasis can lead fulfilling lives.

.jpg)