Introduction:
Ultrasound technology is a non-invasive diagnostic tool that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the inside of the body. It is widely used in various medical specialties, including obstetrics, cardiology, and radiology, to diagnose and monitor a wide range of conditions.
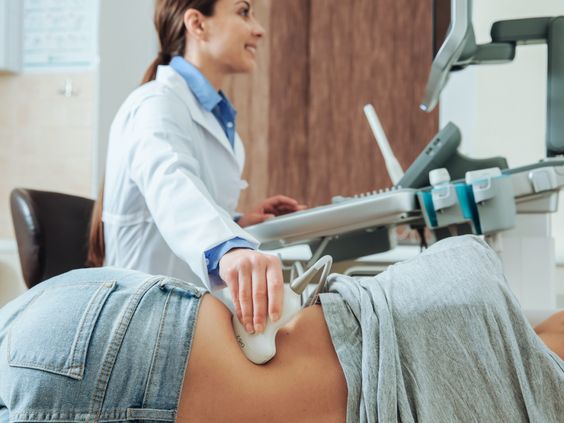

Ultrasound works by emitting sound waves from a transducer, a small handheld device, placed on the skin. These sound waves travel through the body and are reflected back to the transducer when they encounter different tissues and organs. The transducer then converts these reflected sound waves into electrical signals, which are processed by a computer to generate real-time images.
How Ultrasound Creates Images:
The principle behind ultrasound imaging lies in the varying acoustic properties of different tissues. When sound waves encounter a boundary between two tissues with different densities or acoustic impedances, some of the waves are reflected back to the transducer, while others continue to travel deeper into the body. The amount of reflection depends on the difference in acoustic impedance between the two tissues. By measuring the time it takes for the sound waves to return to the transducer and the intensity of the reflected waves, the ultrasound machine can determine the location, size, and shape of organs and tissues.
Medical Applications of Ultrasound:
Ultrasound has a wide range of applications in medicine, including:
- Obstetrics: Monitoring fetal development, detecting fetal abnormalities, and guiding procedures such as amniocentesis.
- Cardiology: Evaluating heart function, detecting heart valve problems, and assessing blood flow in major arteries and veins.
- Radiology: Diagnosing and monitoring conditions affecting organs such as the liver, kidneys, pancreas, and thyroid.
- Gastroenterology: Identifying gallstones, assessing the pancreas, and guiding biopsies.
- Urology: Evaluating the kidneys, bladder, and prostate.
- Musculoskeletal: Diagnosing muscle and tendon injuries, joint effusions, and ligament tears.
Advantages of Ultrasound:
Ultrasound offers several advantages over other imaging modalities:
- Non-invasive: Ultrasound does not involve ionizing radiation, making it a safe option for patients of all ages, including pregnant women.
- Real-time imaging: Ultrasound provides real-time images, allowing physicians to observe moving structures, such as the beating heart or blood flow in vessels.
- Widely available: Ultrasound machines are relatively inexpensive and portable, making them accessible in various healthcare settings.
- Cost-effective: Ultrasound is often more cost-effective than other imaging techniques.
Conclusion:
Ultrasound technology plays a crucial role in modern medicine, providing a non-invasive, safe, and effective way to diagnose and monitor a wide range of medical conditions. Its versatility, real-time imaging capabilities, and cost-effectiveness make it an indispensable tool in various medical specialties.